“Neuroplasticity knows no bounds; it is a lifelong journey of growth, learning, and personal transformation.” – Dr. Andrew Huberman whose quote we ended our last EPISODE on a “Deeper Diver into Neuroplasticity.”
On today’s episode we will review:
✔ Tips for regrowing our brain cells (neurogenesis)
✔ A reminder of what prevents neurogenesis and hurts our brain and what we can do to help increase neurogenesis in our brain.
✔ What’s the Difference Between Neuroplasticity and Neurogenesis?
✔ What’s the Controversy with Neurogenesis?
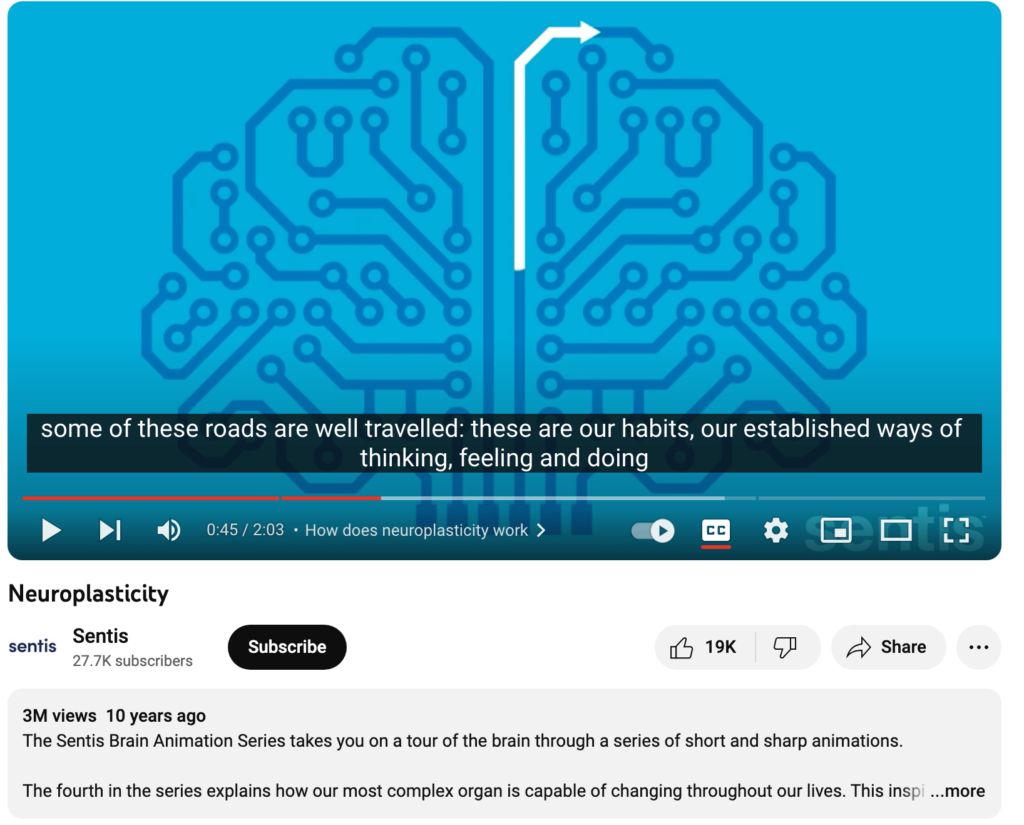
What’s the difference between Neuroplasticity, that we covered on EPISODE #302[i] (that knows no bounds) that’s defined as “the ability of the brain to form new connections and pathways and change how it’s circuits are wired; (as shown so well in the Sentis YouTube video that gives us a representation of these pathways visually, and what they look like in our brain when we create NEW pathways).[ii] This we KNOW we can do throughout our lifetime, (while) neurogenesis is the even more amazing ability for the brain to grow new neurons (Bergland, 2017).[iii] And on today’s episode #303, we will take a closer look at “What Exactly IS Neurogenesis and Why is it Controversial Among Neuroscientists.”[iv]
Welcome back to The Neuroscience Meets Social and Emotional Learning Podcast, where we connect the science-based evidence behind social and emotional learning (that’s finally being taught in our schools today) and emotional intelligence training (used in our modern workplaces) for improved well-being, achievement, productivity and results—using what I saw as the missing link (since we weren’t taught this when we were growing up in school), the application of practical neuroscience. I’m Andrea Samadi, an author, and an educator with a passion for learning and launched this podcast 5 years ago with the goal of bringing ALL the leading experts together (in one place) to uncover the most current research that would back up how the brain learns best, taking us ALL to new, and often unimaginable heights.
For today’s episode #303, and in keeping with our Season Theme of Going Back to the Basics, to take our learning to new heights, I’m going back to EPISODE #141[v] on “Neurogenesis: What Helps or Hurts our Brain Cells” because it became clear to me that while researching for our last episode that Neuroplasticity and Neurogenesis are closely connected, but the former is widely accepted, while the latter holds some controversy.
In our first episode on neurogenesis, we looked at:
✔ Tips for regrowing our brain cells (neurogenesis)
✔ A reminder of what prevents neurogenesis and hurts our brain and what we can do to help increase neurogenesis in our brain.
Dr. Andrew Huberman on Neurogenesis
While researching Dr. Huberman’s work last week on neuroplasticity, he mentioned that there was “bad news” with “neurogenesis” and that many people think that they can exercise and add “new neurons” in the brain and “that after age 14, the human nervous system adds few new neurons.”[vi] He said that “in rodents neurogenesis could occur but in humans it was less obvious” and “that while we can’t add new neurons, we can change our nervous system”[vii] and dives deeper into the definition of neuroplasticity and why this holds no bounds. Now I’m starting to see the controversy in this topic, as I went back to my first look at Neurogenesis.
Dr. David Perlmutter (a board-certified neurologist) on Neurogenesis and Dr. John Ratey, the author of Spark: The Revolutionary New Science of Exercise and the Brain
To open up EP 141 from June 2021, I quoted Dr. David Perlmutter, a board-certified neurologist and six-time New York Times bestselling author who said “the best way to increase neurogenesis (regrow your brain cells) is “when your body produces more BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor” (Dr. David Perlmutter) and we covered this topic deeply on EP 274[viii] “What New With BDNF: Building a Faster, Stronger and More Resilient Brain.” I even remember Dr. John Ratey[ix] the author of the book Spark: The Revolutionary New Science of Exercise and the Brain said that BDNF was like “Miracle-Gro for the brain” (you can’t forget some of the things some people say over the years and he cites a paper where he talked about how brain cells “do grow back in the hippocampus (and that in the study he sited), they saw while looking at the brains of terminally ill patients who had donated their body to science (Cancer patients who had been injected with a dye that shows up in proliferating cells so that the spread of the disease could be tracked) found their hippocampi were packed with dye marker, proof that the neurons were dividing and propagating—a process called neurogenesis.”[x] (Page 48, Spark)
Dr. Ratey’s book Spark, talks about “how to kick-start neurogenesis” and where the research began, causing me to think back to Dr. Perlmutter’s website where he mentioned that BDNF causes neurogenesis or new cells to form in our brain. He cites the studies that show how “exercise training increases the size of the hippocampus and improves memory” exactly what Dr. Ratey saw that made such a huge difference with those students he worked with at Naperville High School.
Dr. Perlmutter’s video talks about the study that showed that after 1 year of aerobic exercise, “exercisers had a marked increase in BDNF, and they showed substantial improvement in memory function.”[xi]
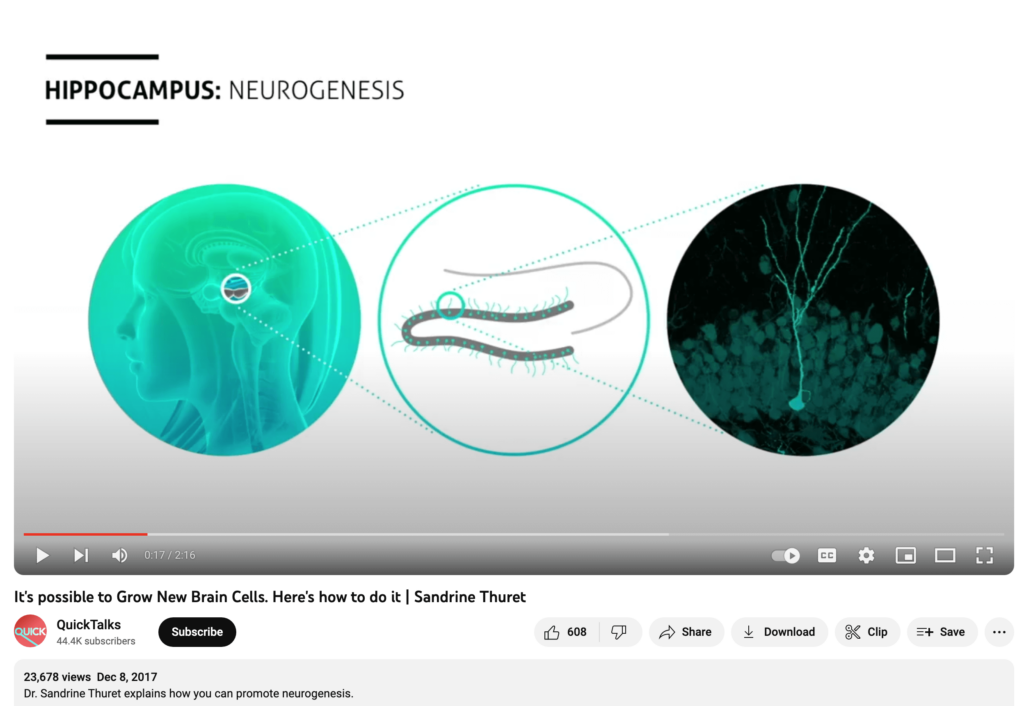
Then I found another video I watched in our last episode from Sandrine Thuret called “It’s Possible to Grow New Brain Cells” where she said that “we produce 700 new neurons a day in the hippocampus”[xii]
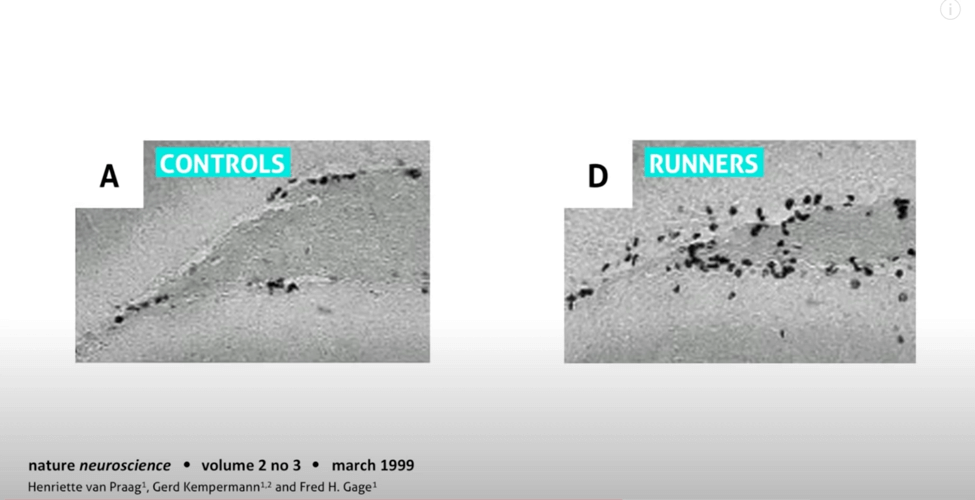
Sandrine Thuret’s TED TALK lists many ways you can grow new brain cells (the highlighted words) with intermittent fasting, flavonoids (found in dark chocolate) and caffeine being a few evidence-based strategies. Conversely, she mentions a diet high in saturated fat, sugar or ethanol, will have a negative impact on neurogenesis. She even showed a study (from Praag, Kepermann and Gage) where rats who were runners shows an increase in neurogenesis vs the control group who were non-runners that Dr. Ratey talks about in his book Spark.
What Does This All Mean? Where’s the Controversy? Neuroplasticity vs Neurogenesis
To review and conclude this episode on “Diving Deeper into Neuroplasticity and Neurogenesis” I think we’ve got a clear picture of how neuroplasticity works from our last episode, (by making a conscious effort to build new neural pathways in our brain when we learn something new) but the topic of how we can grow new neurons seems to be where the controversy exists. It seems like this is only possible in the hippocampus but I still do wonder why a neurologist like Dr. Perlmutter says neurogenesis is possible through exercise[xiii], while another respected neuroscientist’s stance is that “in humans this is less obvious.”[xiv] This is where the deep learning comes into our study, and being open to what we might uncover here. If we aren’t continually questioning what we are learning, then we aren’t thinking at all.
Mark Waldman’s AHA Moment: What Neuroplasticity Is and Isn’t
While thinking about why neurogenesis is “less obvious” in humans, as it might be in rodents, like Sandrine Thuret’s TED TALK covered, and even Dr. Ratey took the same rodent study and made a comparison to the students at Naperville whose test scores improved after running. Then I remembered my mentor Mark Waldman made me think deeply about this when he wrote about “What Neuroplasticity Is and Isn’t”[xv] where he explained an article “Adult Neurogenesis in Humans”[xvi] that ended up being my AHA Moment of learning here.
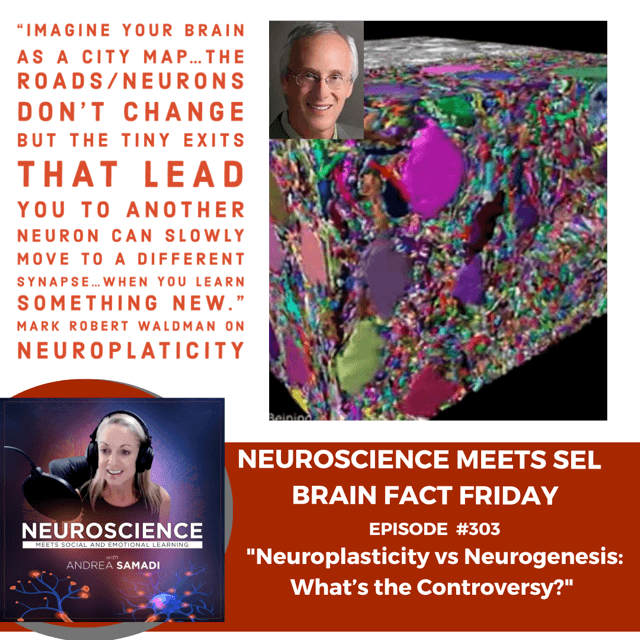
He said to “imagine the brain as a city map, and instead of there being 214 streets in Manhattan, imagine that it had a million streets! No room for buildings, just streets winding and weaving east to west, north to south, up and down and diagonal, all woven together like a giant hairball. Each city is a brain function – vision, movement, memory, imagination, feelings, etc. – and the entire state of New York would have cities upon cities woven together on top and alongside each other. Those billions of roads have trillions of cul-de-sacs which are the synapses.
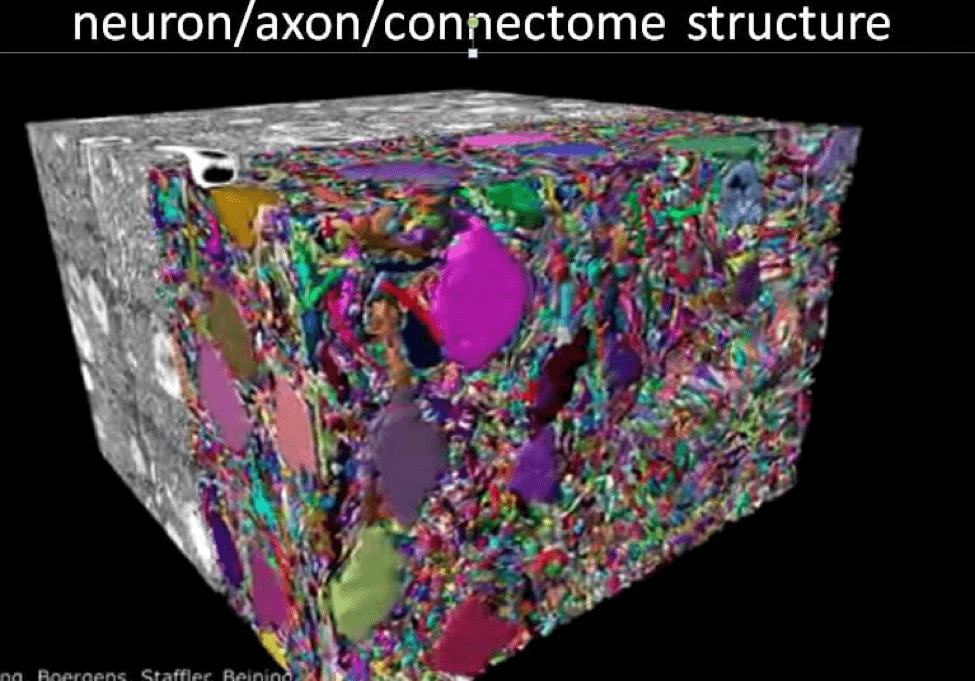
Can you visualize that? Above is an actual slice of a thousandth of a millimeter of mouse brain: Everything is jam packed but you the traveler can decide which road or neural pathway to take in order to reach a specific destination to help you perform some action of achieve a particular goal. The fastest your brain can process information is about 60 bits per second, and he guesses that any cognitive function would be traveling around 2,000 miles per hour down those roadways in your brain! Now we can ACCURATELY visualize what plasticity looks like in the adult human brain a bit deeper than what we first looked at the Sentis YouTube with the connections in our brain this way. This was my FIRST look at neuroplasticity, and this video came out 10 years ago.
Look at the difference with this image that came from the research paper Mark Waldman read on “Adult Neurogenesis in Humans” that changed his thinking about neuroplasticity and neurogenesis. He said “the roads/neurons don’t change but the tiny exits that lead you to another neuron can slowly move to a different synapse, similar to how switch-ways work on a railroad track. That’s where synaptic plasticity takes place and that’s what happens when you learn something new: You’re beginning to find new pathways that create different decisions and behaviors.
Waldman went on to point out some main take-aways from this Paper on Neuroplasticity but the ones I want to mention are that
- “This kind of plasticity does not add or replace neurons.”
- “the exception is a process called “adult neurogenesis” conferred by active stem cell niches…in restricted regions [olfactory bulb & hippocampus]” (Confirmed by Dr. Huberman’s research) [xvii]
- “After 60 years of intense research and more than 10,000 peer-reviewed publications, we still do not know if our brain maintains such capability.”
- Synaptic changes are very slow, involved with learning and brain repair.
- Stem cell-driven “adult neurogenesis” is still far in the future.
RESEARCH FROM: La Rosa C, Parolisi R, Bonfanti L. Brain Structural Plasticity: From Adult Neurogenesis to Immature Neurons. Front Neurosci. 2020 Feb 4;14:75.
Review and Conclusion: Neuroplasticity vs Neurogenesis: Uncovering the Controversy
So now I’ve opened up a bit more as to “WHY” this topic holds controversy among neuroscientists, and I think while this is a good start at explaining how Neuroplasticity is different than Neurogenesis, I do want to leave this topic open, to come back to at a later date, and see what else we can add to our understanding
In the meantime, I’ll continue to read, learn and think of how this learning can apply to our daily life. While researching this topic, I found an article I like called What is Neuroplasticity[xviii] written just this past April 2023. It explains neuroplasticity thoroughly, and how it applies to learning, a growth mindset, and how it changes as we age. It covers neuroplasticity and how it can help with anxiety, which made me think back to when we changed our brain with Dr. Caroline Leaf’s 5 Step Process for Cleaning Up Our Mental Mess on EP #299.[xix] It even covers neuroplasticity exercises for treating chronic pain that took me back to our interview with Ashok Gupta[xx] a well-known brain-training neuroplasticity expert who taught us how to use our brain and mind to manage chronic pain and illness.
At the end of this article there are YouTube videos from many of the experts we’ve covered on this podcast like Dr. Daniel Amen, Dr. Joe Dispenza, and books from Dr. Caroline Leaf, and Norman Doidge.
But what was missing, was more about Neurogenesis and how we can change actually change our brain, not just re-wire the pathways in it, there were a bunch of quotes at the end of this article but they were all about neuroplasticity.
Neuroplasticity Quotes
Among other things, neuroplasticity means that emotions such as happiness and compassion can be cultivated in much the same way that a person can learn through repetition to play golf and basketball or master a musical instrument, and that such practice changes the activity and physical aspects of specific brain areas.–Andrew Weil
Because of the power of neuroplasticity, you can, in fact, reframe your world and rewire your brain so that you are more objective. You have the power to see things as they are so that you can respond thoughtfully, deliberately, and effectively to everything you experience.–Elizabeth Thornton
Any man could, if he were so inclined, be the sculptor of his own brain.–Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Meditation invokes that which is known in neuroscience as neuroplasticity; which is the loosening of the old nerve cells or hardwiring in the brain, to make space for the new to emerge.–Craig Krishna
Everything having to do with human training and education has to be re-examined in light of neuroplasticity.–Norman Doidge
Neurons that fire together wire together.–Donald O. Hebb (Dr. Huberman would say this came from Carla Shatz)
Brains are tricky and adaptable organs. For all the ‘neuroplasticity’ allowing our brains to reconfigure themselves to the biases of our computers, we are just as neuroplastic in our ability to eventually recover and adapt.–Douglas Rushkoff
Our brains renew themselves throughout life to an extent previously thought not possible.–Michael S. Gazzaniga
Our minds have the incredible capacity to both alter the strength of connections among neurons, essentially rewiring them, and create entirely new pathways. (It makes a computer, which cannot create new hardware when its system crashes, seem fixed and helpless).–Susannah Cahalan
Where are the quotes for Neurogenesis?
Like the quote I found from Dr. Perlmutter who said “We can regrow brain cells and retain this ability throughout our entire lifetime.”
- Is this only possible in our hippocampus? Or will science someday reveal that adult neurogenesis is possible like what Mark Walman mentioned with stem-cell adult neurogenesis that he thinks is far in the future?
Until we know for sure, I’m going to stick with doing what I know helps my brain according to Dr. Perlmutter’s work, and Sandrine Thuret’s TEDTALK where she says by doing certain things like the words she’s highlighted in her graphic, we can create neurogenesis that’s important for learning and memory, and I’ll avoid the non-highlighted words that she says prevents neurogenesis. And I’ll come back to this episode at a future date to see what else we can add to accelerate our understanding of “Neuroplasticity vs Neurogenesis.” With that thought, I hope this episode has made you think deeper about your brain, especially when it comes to making choices that we know can improve our ability to build a stronger, more resilient brain by doing what helps it (and our brain cells) instead of what hurts it, and I’ll see you next week.
REFERENCES:
[i] https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/brain-fact-friday-and-a-deeper-dive-into-applying-neuroplasticity-to-learn-something-new/
[ii] Neuroplasticity Published on YouTube November 6, 2012 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ELpfYCZa87g
[iii] What is Neuroplasticity: A Psychologist Explains [14+ Tools] by Courtney E Ackerman, MA, Published July 25, 2018, Scientifically reviewed by Melissa Madeson, Ph.D.
https://positivepsychology.com/neuroplasticity/#google_vignette
[iv] Adult Neurogenesis in Human: A Review of Basic Concepts, History, Current Research, and Clinical Implications Published May 1, 2019 by Ashutosh Kumar, MD. et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6659986/
[v] https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/brain-fact-friday-on-neurogenesis-what-hurts-or-helps-your-brain-cells/
[vi] Dr. Andrew Huberman Lab Podcast EPISODE #6 “How to Focus to Change Your Brain” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LG53Vxum0as
[vii] IBID
[viii] https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/brain-fact-friday-what-s-new-with-bdnf-building-a-faster-stronger-more-resilient-brain/
[ix] Neuroscience Meets Social and Emotional Learning Podcast EPISODE#116 with Dr. John Ratey on “The Revolutionary New Science of Exercise and the Brain” https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/best-selling-author-john-j-ratey-md-on-the-revolutionary-new-science-of-exercise-and-the-brain/
[x] Spark: The Revolutionary New Science of Exercise and the Brain by John J. Ratey, MD (January 10, 2008) https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07D7GQ887/ref=dp-kindle-redirect?_encoding=UTF8&btkr=1
[xi] https://www.drperlmutter.com/neurogenesis-re-grow-new-brain-cells-exercise/
[xii]Is It Possible to Grow New Brain Cells by Sandrine Thuret published Dec. 8th, 2017 https://capture.dropbox.com/W0af55YnE3LhDb0M
[xiii] https://www.drperlmutter.com/neurogenesis-re-grow-new-brain-cells-exercise/
[xiv] Dr. Andrew Huberman Lab Podcast EPISODE #6 “How to Focus to Change Your Brain” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LG53Vxum0as
[xv] Mark Waldman “What Neuroplasticity is and isn’t” Published on Facebook Nov. 10, 2020 https://www.facebook.com/photo?fbid=1300824310263746&set=a.112516002427922
[xvi] Adult Neurogenesis in Human: A Review of Basic Concepts, History, Current Research, and Clinical Implications Published May 1, 2019 by Ashutosh Kumar, MD. et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6659986/
[xvii] Dr. Andrew Huberman Lab Podcast EPISODE #6 “How to Focus to Change Your Brain” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LG53Vxum0as
[xviii] What is Neuroplasticity: A Psychologist Explains [14+ Tools] by Courtney E Ackerman, MA, Published July 25, 2018, Scientifically reviewed by Melissa Madeson, Ph.D.
https://positivepsychology.com/neuroplasticity/#google_vignette
[xix] https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/brain-fact-friday-on-a-deep-dive-into-dr-carolyn-leaf-s-5-scientifically-proven-steps-to-clean-up-our-mental-mess-so-we-can-help-our-children/
[xx] https://andreasamadi.podbean.com/e/ashok-gupta-on-heath-and-happiness-getting-to-the-root-of-chronic-pain-and-illness-long-covid-fibromyalgia-chronic-fatigue-and-others/
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS